a. Introduction
In this workshop, you will experiment how to run large-scale Monte Carlo simulations with the elastic infrastructure using AWS Batch. In the meantime, you will use AWS Lambda to run smaller workload requiring fast turnaround with the same container image used for AWS Batch. You can also choose to deploy the same infrastructure to a second region with the same procedure to meet compliance and resilience requirements.
You are familiar with AWS Batch and its benefits after finishing previous sections. Now we introduce AWS Lambda briefly as another compute service from AWS. You will also use Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) for file storage and S3 Event Notifications to start simulation jobs when the input files are uploaded to the S3 input bucket.
About AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda is a serverless, event-driven compute service that lets you run code for virtually any type of application or backend service without provisioning or managing servers. You can trigger Lambda from over 200 AWS services and software as a service (SaaS) applications, and only pay for what you use.
In addition to start running applications within seconds of an trigger event, there are several more benefits by choosing AWS Lambda. Some of them are listed below:
- Run code without provisioning or managing infrastructure
- Event driven application execution
- Built-in fault tolerance
- Package and deploy functions as container images
- Scale to match demand
About Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3)
Amazon S3 is an object storage service offering industry-leading scalability, data availability, security, and performance. Customers of all sizes and industries can store and protect any amount of data for virtually any use case, such as data lakes, cloud-native applications, and mobile apps. With cost-effective storage classes and easy-to-use management features, you can optimize costs, organize data, and configure fine-tuned access controls to meet specific business, organizational, and compliance requirements.
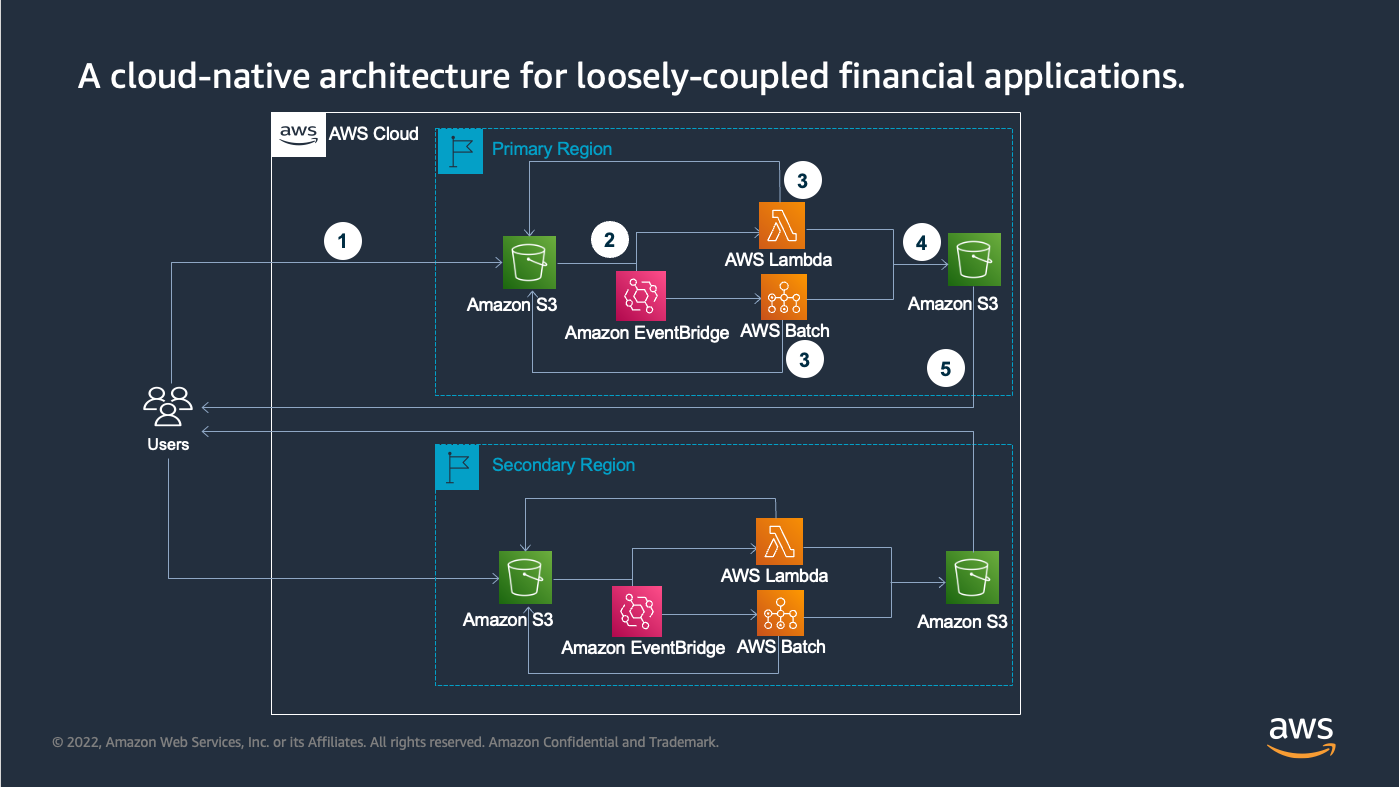
Application operation workflow steps:
- Upload an input CSV file with financial asset information to S3 bucket using timestamp as S3 prefix, which could be used as job ID for tracking purpose.
- A lambda job is triggered with S3 prefix “fast/”, and a Batch job is triggered through EventBridge with S3 prefix “normal/”.
- The job will be split to multiple input files and put on S3 to run in parallel if above a threshold. For Lambda, the same event-driven process is used to run the job; for Batch, jobs run in parallel with Batch job arrays for efficiency. The input file is processed if it is under a threshold (configurable through environment variable), e.g., 10 equities.
- The result files are put on an S3 bucket with the same job ID directory.
- Users get result back by copying from S3 bucket.