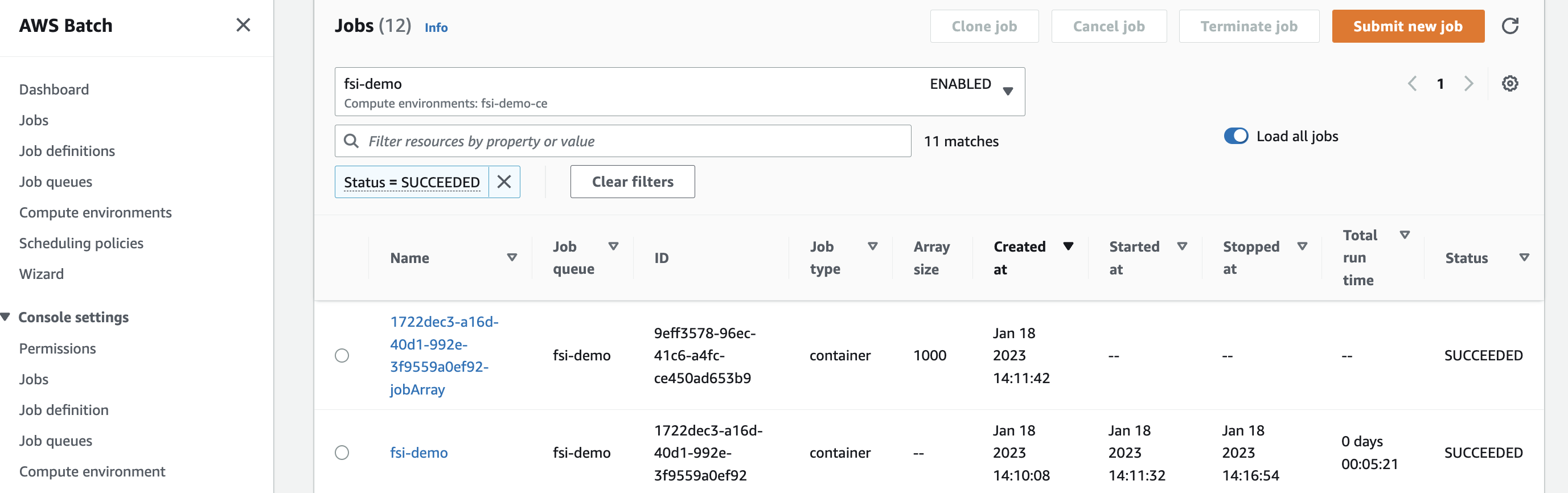
2. Run Simulations with 1000 vCPUs using AWS Batch
You have finished small tests with both Lambda and Batch, now you can run a job with 100k equities using AWS Batch on this distributed system. While Lambda can scale to thousands of CPUs to run jobs with very low startup time, the primary reasons of choosing Batch for large-scale workload are cost-effective and the ability to scale to millions of CPUs. The total cost of this experiment is under $5 with on-demand EC2 instances. If you are running it on your own account, make sure the EC2 quota for maximum number of vCPUs is enough to reach the concurrency: https://console.aws.amazon.com/servicequotas/home/services/ec2/quotas
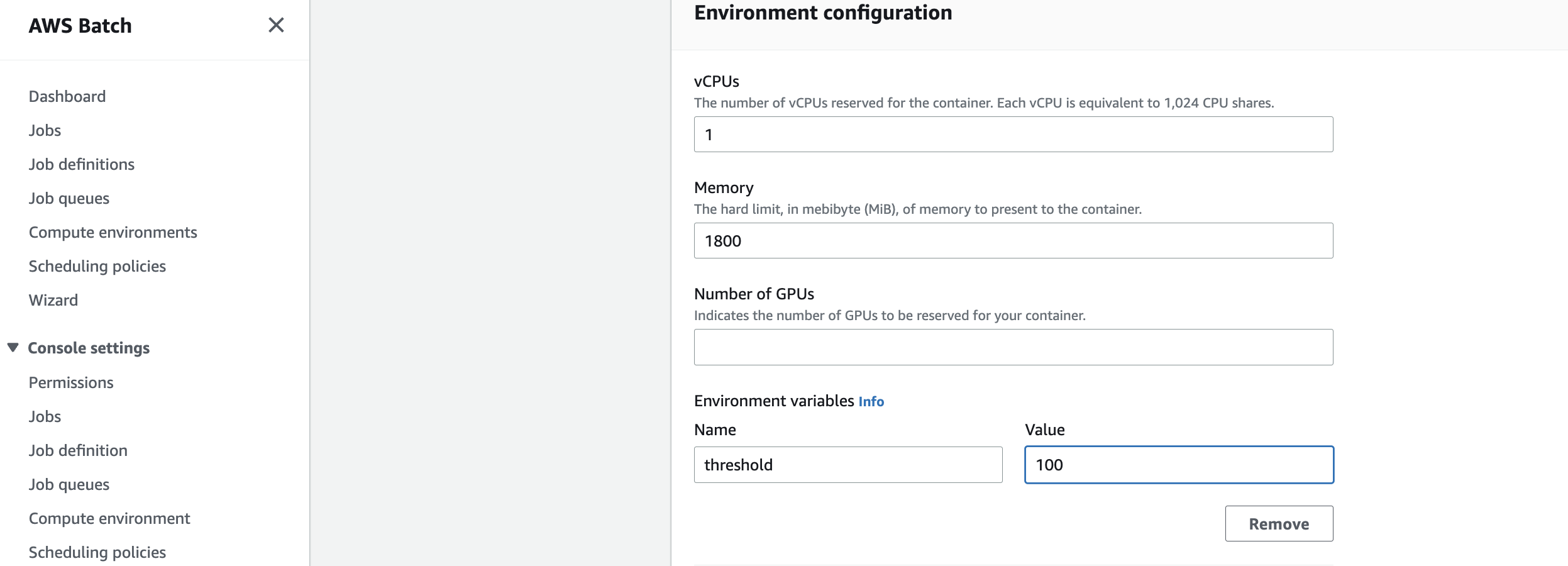
Before you start to run large-scale jobs, you can adjust the threshold to a larger number, so it will take more time for each job for better cost efficiency, as EC2 used for Batch is billed in one-second increments, with a minimum of 60 seconds. First, find the “fsi-demo” job definition from the Batch job definition console. Then click “Create revision” after selecting the job definition, and update the threshold to “100” in the second page with other fields unchanged as the screenshot below:
Increase job distribution threshold to 100
After clicking “Create job definition” in the last page, you can upload a new file to the input S3 bucket that will trigger a new large job to process the data contained in the file with following command.
Run an AWS Batch job of 100k equities
curl -o Data/EquityOption-100k.csv https://raw.githubusercontent.com/aws-samples/aws-hpc-tutorials/batch/static/scripts/batch-lambda/Data/EquityOption-100k.csv
aws s3 cp Data/EquityOption-100k.csv s3://$INPUT_BUCKET/normal/100k/
AWS Batch console screenshot showing the whole workload with a job array is finished within 10 minutes on 1000 vCPUs